Waves
Vibration
The cyclical motion of an object about an equilibrium point
Mechanical Wave
The transfer of energy through a material by particle vibration.
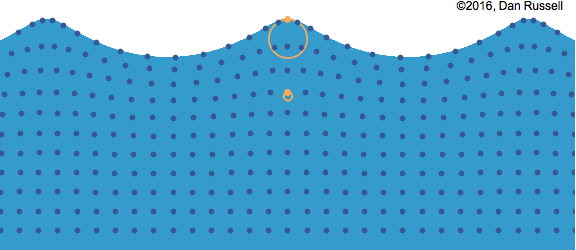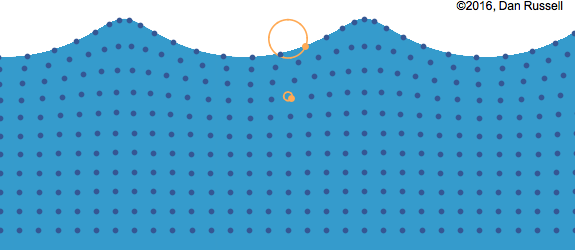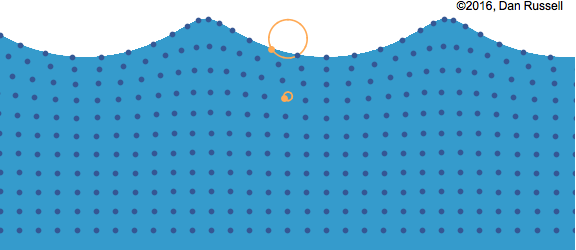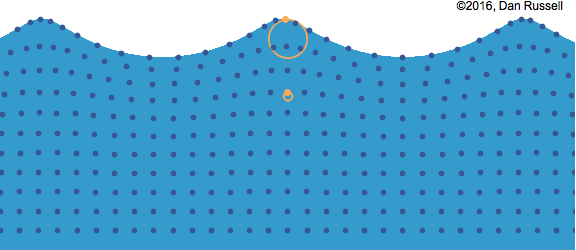
- Water waves move away from the point of the original disturbance.
- The water itself is not moving; rather it is a rearrangement of the water’s surface.
- We could consider a wave to be the motion of a disturbance
Net Motion
The displacement of a particle over a certain time interval.
- After a wave has passed through a medium, the particles return to their original location so ideally, their net displacement is zero.
- Therefore, no work is done on them by the wave – no energy is lost and it can continue indefinitely.
What is a Medium?
The material through which a mechanical wave travels. (Solid, Liquid, Gas)
- A vibration is able to travel through a medium because each molecule in the medium is connected to neighbouring molecules by intermolecular forces.
- This allows a mechanical wave to be one of the most efficient forms of energy transmission in nature.
Efficiency of Vibration Transfer
| Solid | LIquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|
| High | very good | Low |
Transverse Waves
The direction of the wave is perpendicular to the motion of the source Ex. Water

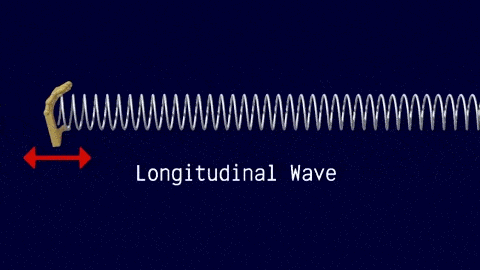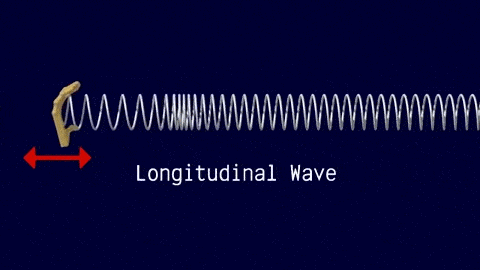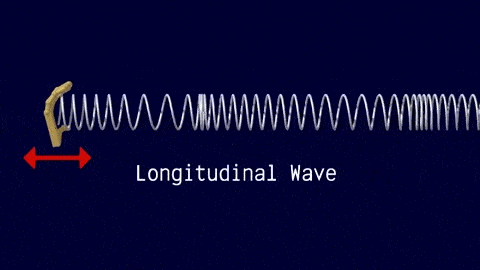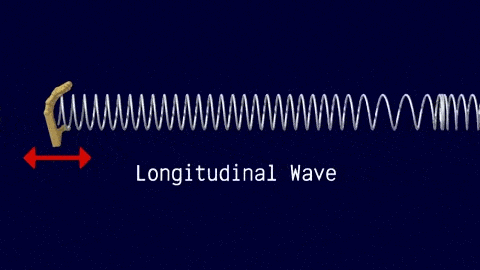
Longitudinal Waves
The travel of the wave is in the same direction to the motion of the source.