The phenomenon that occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. The concentration of all participants stays the same.
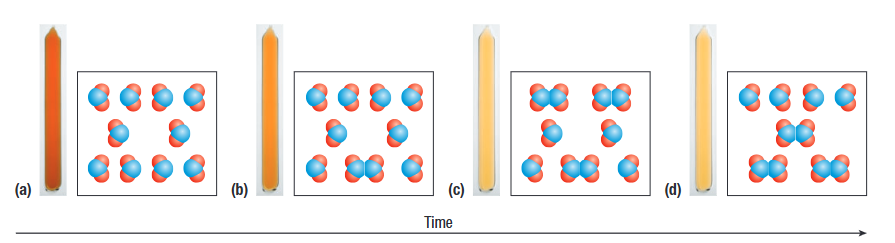
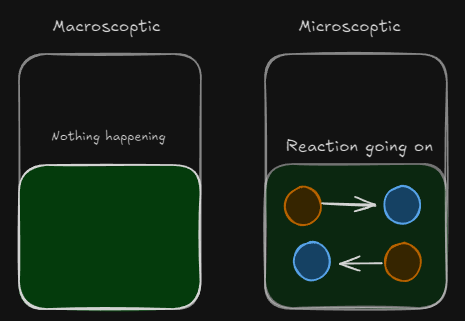
In this example, the colour of the substance remains constant after c) because the system has reached equilibrium, even though forward and reverse reactions are taking place
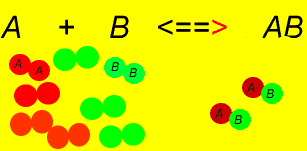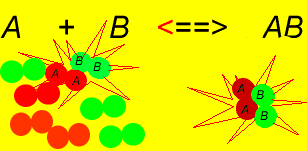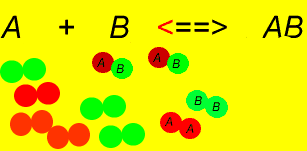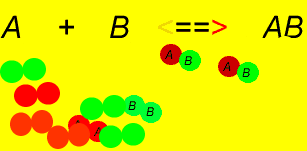
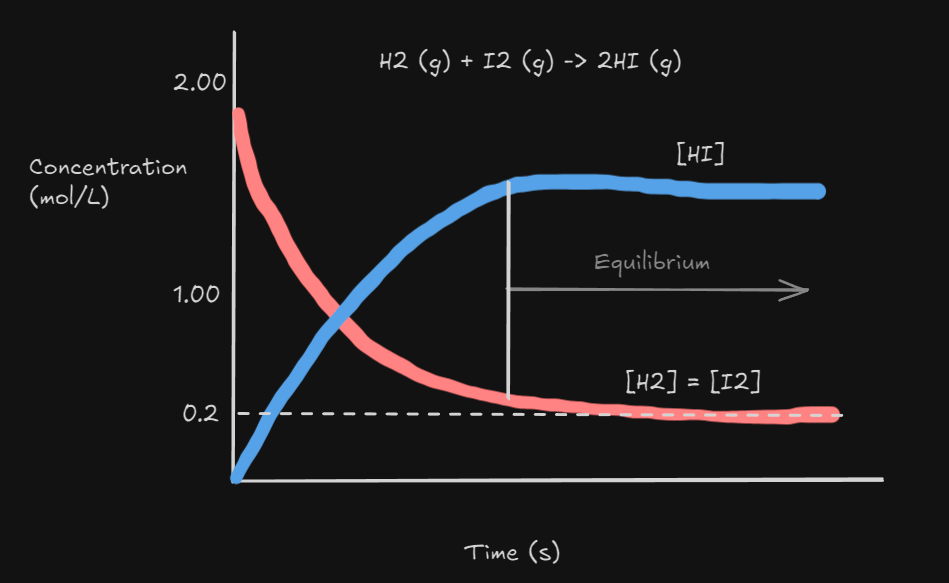 In this example. is initially zero
and decrease as they react to produce (Forward Reaction)
In this example. is initially zero
and decrease as they react to produce (Forward Reaction)
- As increases, more of these molecules will collide to make and molecules (Reverse Reaction)
- Eventually a point is reached where the rate of the forward reaction = rate of the reverse reaction and the concentrations of all participants remains unchanged.
Characteristics
- There is some amount of every reactant and product present in the system at equilibrium
- The system is dynamic at the microscopic level because both forward and reverse reactions are going on at the same time. The system is at equilibrium because the rate of the forward reaction = rate of the reverse reaction
- At the macroscopic level, the system does not change (eg. colour, pressure, volume, temperature, concentration)
- The system must be closed
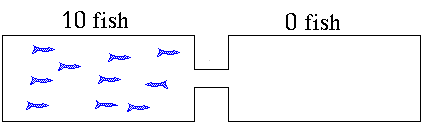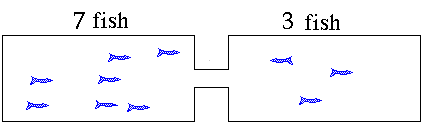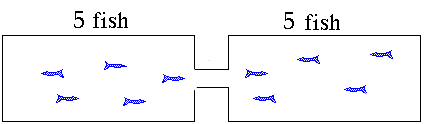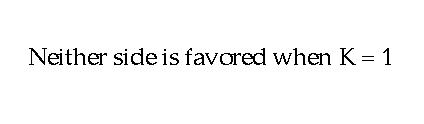
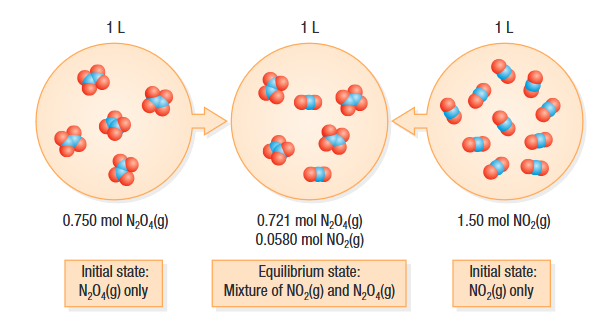 In this example, the composition of the mixture is the same no matter which gas you start with
In this example, the composition of the mixture is the same no matter which gas you start with
Stress
A change in the environmental conditions of a system ex. Adding heat
Le Chatelier’s Principle
When an equilibrium is subject to stress, the system reacts to this stress in an attempt to minimize it (since the system is temporarily unbalanced). This stress cannot be entirely removed but if it is not too great, the system may “settle down” into a new equilibrium state.
Factors which Affect a System at Equilibrium
- Concentration changes
- Temperature changes
- Pressure/Volume changes (gaseous systems only)
- Catalysts
- Addition of an inert gas
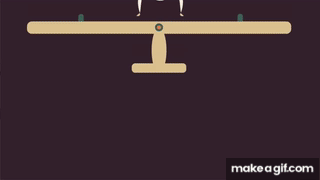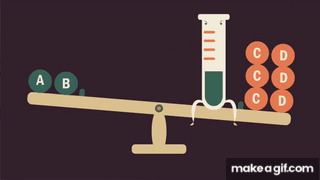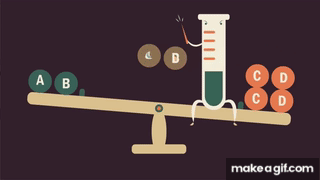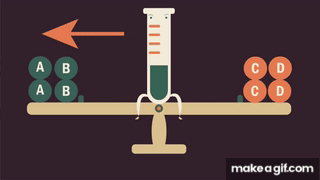
Concentration Change
How does increasing affect equilibrium
Single step mechanism:
Le Chatelier’s principle predicts that the forward reaction will take over when is increased.
- In terms of rate theory, is a term that is found only in the rate law of the forward reaction. If is increased, the forward rate will increase instantaneously with no corresponding increase in the rate of the reverse reaction. Since , the forward reaction takes over.
- As time progresses, and drop, while increases, and the reverse reaction dominates. Eventually, both rates will be equal and a new equilibrium will exist.
Temperature change
Or
- If the temperature is increased
- The system will react so as to remove as as much heat as possible. the forward reaction converts the additional heat into stored energy therefore this reaction takes over. The equilibrium shifts to the right and
- If the temperature is decreased
- The reverse reaction will take over. This reaction can replace the removed heat by shifting the reaction to the left
Pressure or Volume change
Example 1
If the volume of the system decreases, the pressure will increase (Boyle’s Law). The system will try to move in a direction which will minimize pressure. To do this, the system will try to decrease the total number of particles. Since there are 4 particles on the left side (3 molecules & 1 molecule) and 2 particles on the right side (2 molecules), the reaction will shift to the right.
Example 2
In this case, the number of particles is the same on both sides of the equation (2 particles each). As a result, any increase or decrease in pressure will have no effect on the equilibrium however the concentrations of all participants will change.
Catalysts
Le Chatelier’s principle predicts that the addition of a catalyst will have no impact on the rate of a reaction.
CANNOT COMPLETE YET (note not finished)
Addition of Inert Gas
Example:
- If the container is flexible
- The argon causes the container to expand thereby increasing the total volume of the container. As a result, the partial pressure of each component gas decreases (Dalton’s Law). The reaction shifts to the left so as to increase the number of particles.
- If the container is rigid.
- The argon gas causes the total pressure to increase according to Dalton’s Law. However the partial pressure of each component gas remains the same. As a result , the equilibrium will not be affected.