Gravity ()
The “Force” that causes all objects to Accelerate towards the Earth’s surface The rate of gravity does not depend on Mass. Objects of the same Mass fall at the same Speed in a vacuum. It known as an Action at a distance force
The negative indicates deceleration The Acceleration always stays the same, Velocity increases or decreases depending on the direction
Free Fall
Acceleration that occurs when there is no Air Resistance or other Forces affecting the Motion besides gravity
Terminal Velocity
When the Air Resistance on a parachute is equal to the force due to gravity acting on the parachute. It will stope Acceleration and stay at a a constant Velocity
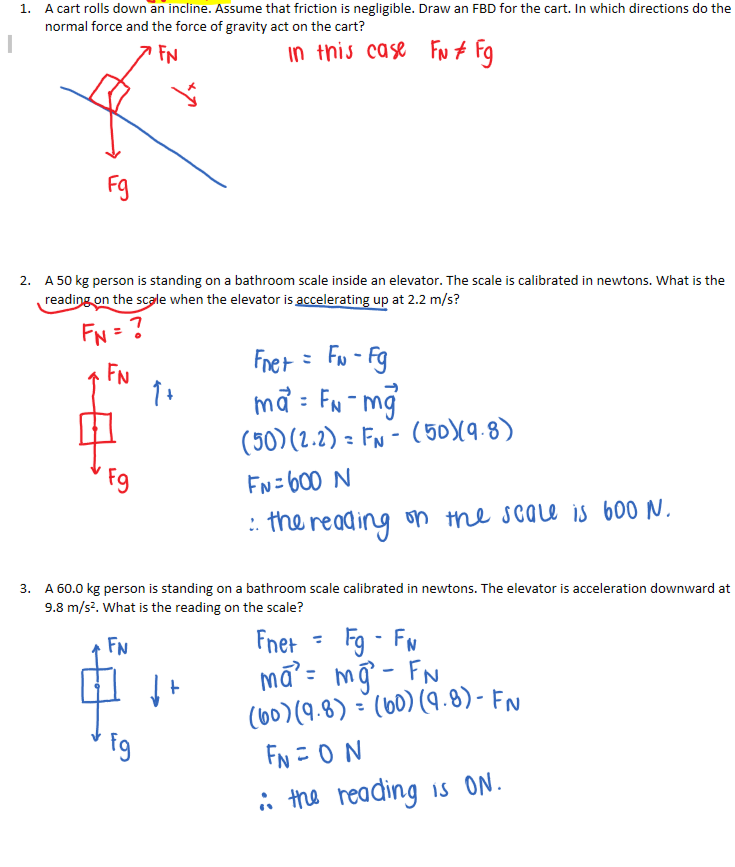
Gravitational Field
The region of influence of gravitational force due to an object.
A field is an influence on a suitable object over a region of space, whether it is an attraction or repulsion
Mass vs Weight
| Mass | Weight |
|---|---|
| The quantity of matter in an object | A measure of the force of gravity acting on an object |
| Can change mass only by adding or removing matter | It depends on the location and the magnitude of Earth’s gravitational field |
| It does not change due to location or gravitational field strength | |
| Unit kg | Unit: Newtons |
 |
Gravity Constant Near Earth
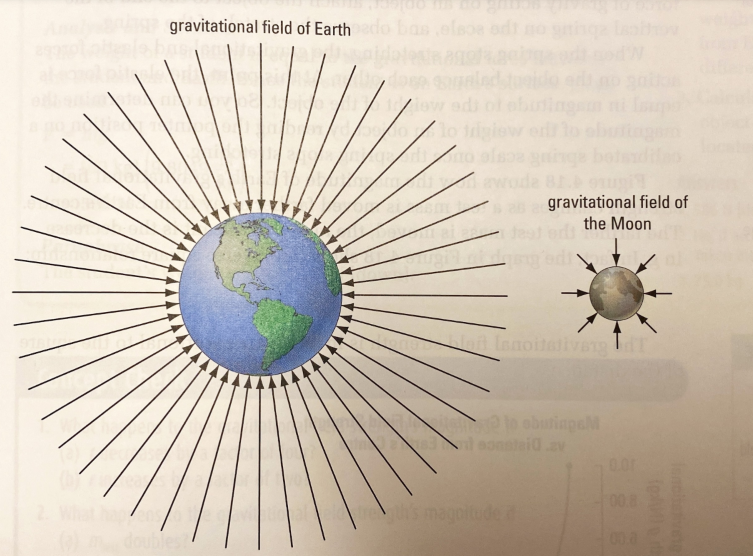
Gravitational Field Strength
It is the gravitational force per unit mass. It decreases as an object is moved farther away from earth’s surface.
For the Earth’s surface, it is 9.8 N/kg [down] On Mount Everest, it is 9.7647 N/kg [down]
The earth bulges at the equator. At the North Pole, it is 9.8322 N/kg [down] At the equator it is 9.7805 N/kg [down]
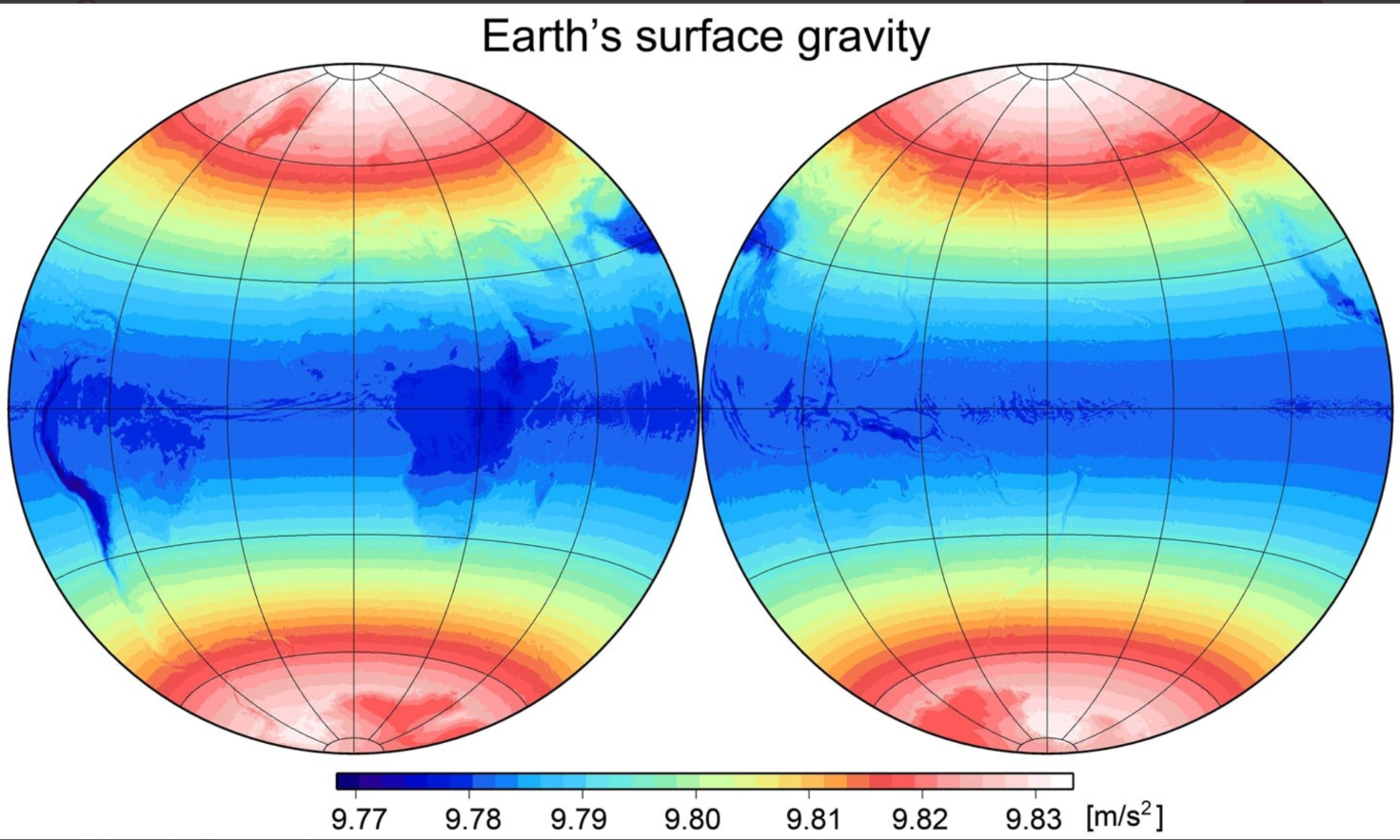
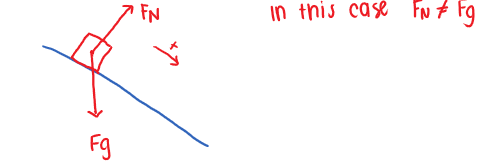
When does the Normal Force = Gravity?
The normal force is only equal to gravity when the degree of rotation is 0
If the object is on a ramp of some kind, then the normal force does not equal gravity.
Examples