Nuclear Fission
The reaction in which a massive nucleus splits into two or more lighter nuclei. This is the reaction used in nuclear reactors to produce Thermal Energy and then electricity.
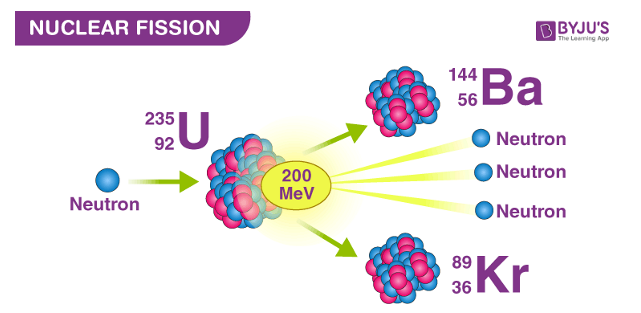
A large amount of energy is released when a nucleus is broken apart. This energy is the difference between the binding energy of the original nucleus and the binding energies of the fission products. The liberated energy takes the form of kinetic energy in the fission products.
Spontaneous Fission
A form of nuclear fission that occurs in very heavy isotopes. It is only seen in nuclei with atomic mass numbers above 230 (elements near Thorium).
It occurs when an unstable isotope splits into two or more smaller nuclei without any external interaction
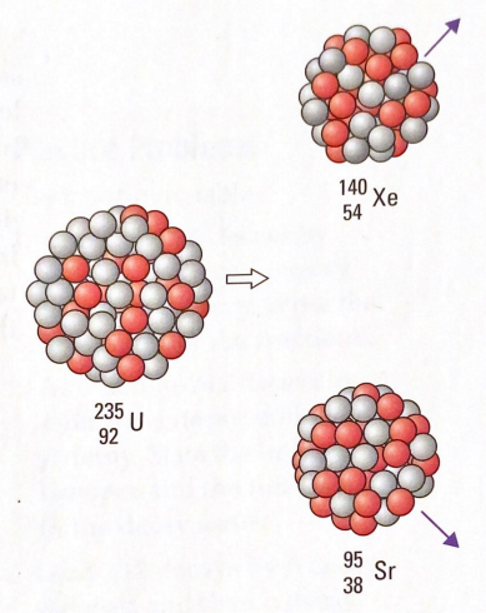
Induced Fission
A fission reaction started when a free neutron is absorbed by a nucleus which forms a highly unstable isotope that breaks up instantly into two lighter nuclei
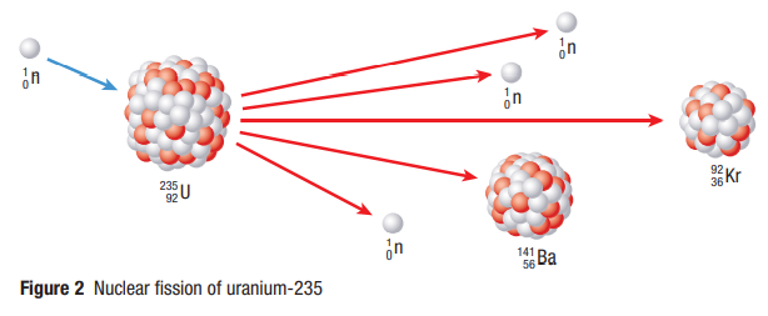
Because neutrons have no charge, free neutrons travel easily through the electron clouds of atoms and may collide with atomic nuclei, inducing fission.
This reaction also emits two or more neutrons which carry off most of the large amount of energy liberated by the reaction.
Gamma Rays are also commonly produced
Mass - Energy Equivalence
Energy and mass are equivalent and interchangeable.
Binding Energy
The energy required to break up the nucleus into its individual protons and neutrons. Bigger Nucleus = Bigger Binding Energy
- In the nucleus, the strong force binds the protons and neutrons (nucleons) tightly together.
Mass Defect
The difference between the mass of each particle in an atom and the atom itself. It exists in the form of energy. Also known as binding energy.
Law of Conservation of Mass-Energy
Mass can be transformed into energy, and energy into mass, such that the total mass-energy in an isolated system remains constant.
Dangers of Fission
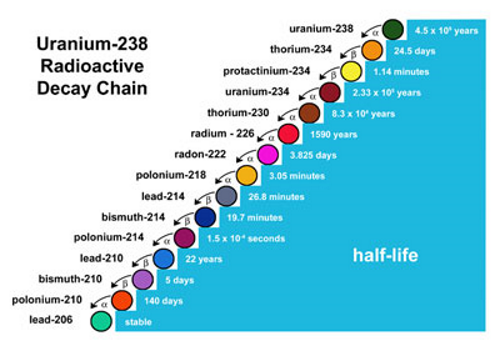
Reactive Decay Series
When a radioactive nucleus decays into a daughter nucleus that is also radioactive, this continues until the nucleus becomes stable with energy released at every step.
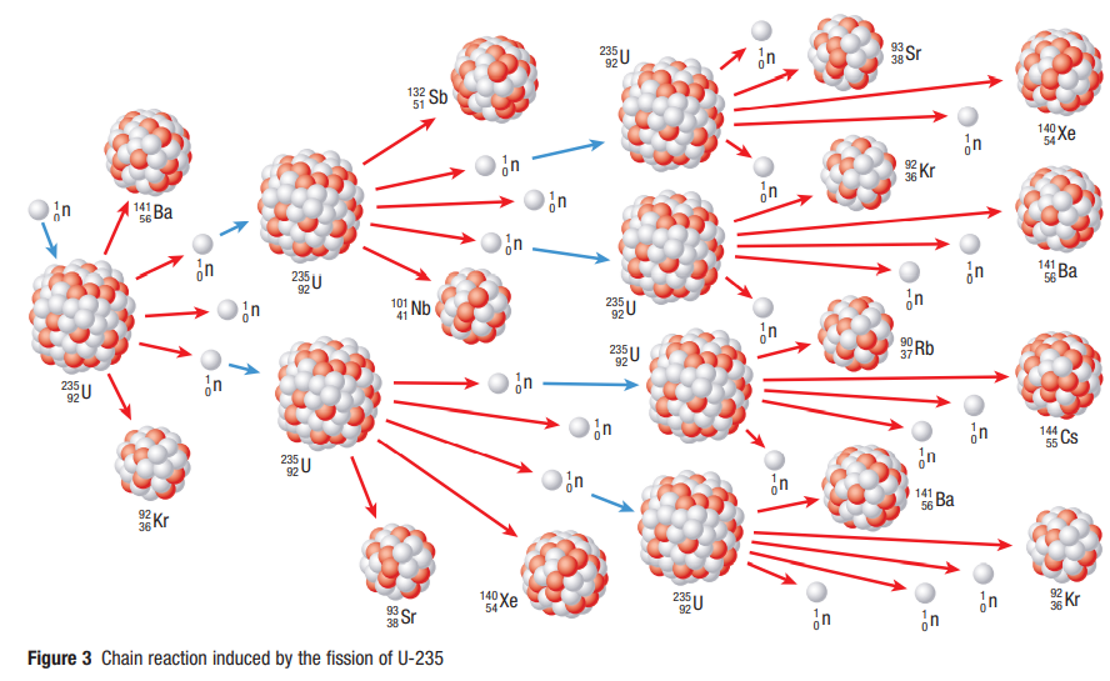
Nuclear Chain Reactions
A series of nuclear fissions that starts with one fission
reaction that produces free neutrons.
These neutrons carry away the energy released by fission