Atoms and Isotopes
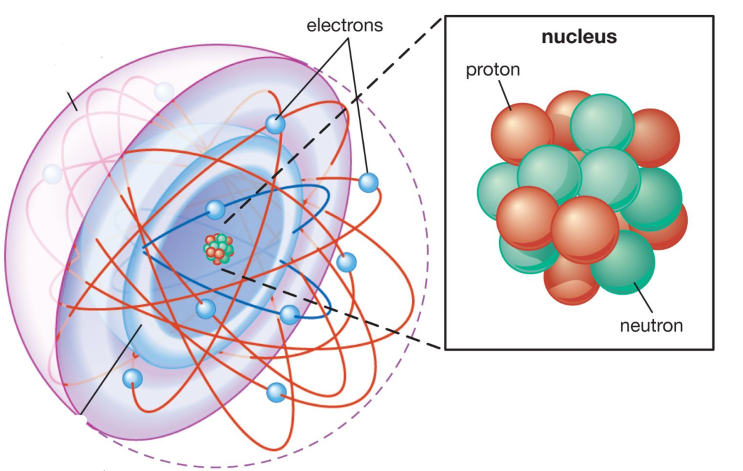 Protons and Neutrons are sometimes referred to as Nucleons
Most of the atom is empty space
Protons and Neutrons are sometimes referred to as Nucleons
Most of the atom is empty space
- Although neutrons have no charge, they help to hold the nucleus together.
- Neutrons add to the strong interaction that holds the nucleus together without adding to the repulsive forces of the positively charged protons
- In general, the more protons there are in the nucleus, the higher the proportion of neutrons needed to hold the nucleus together.
Mass
About 99.9% of the mass of an atom is found in its extremely dense nucleus.
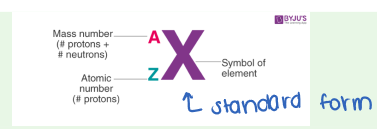
| Atom | Nucleus | Protons/Neutrons | Electrons | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | ||||
 |
Atomic Mass Units ()
The weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of the atom
| Particle | Mass (kg) | Mass (u) |
|---|---|---|
| Electron | 9.109 383 x 10-3 | 5.485 799 x 10-4 |
| Proton | 1.672 622 x 10-27 | 1.007 276 |
| Neutron | 1.674 927 x 10-27 | 1.008 665 |
Neutral Atoms
When the number of protons and neutrons in an atom is the same, it is called a neutral atom.
Antiparticles
Particles that have the same mass but opposite charge
When a particle and its antiparticle meet, they annihilate each other into pure
energy
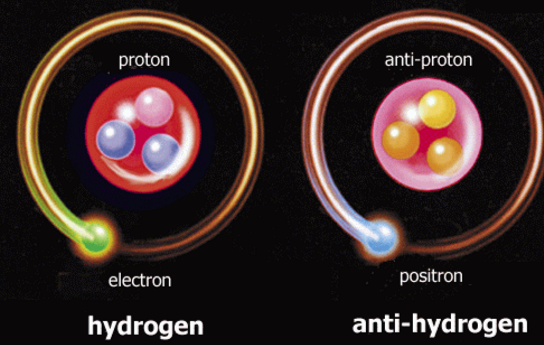
Antimatter is a form of matter composed only of antiparticles
| Particle | Antiparticle |
|---|---|
| Proton | Antiproton |
| Neutron | Antineutron |
| Electron | Positron |
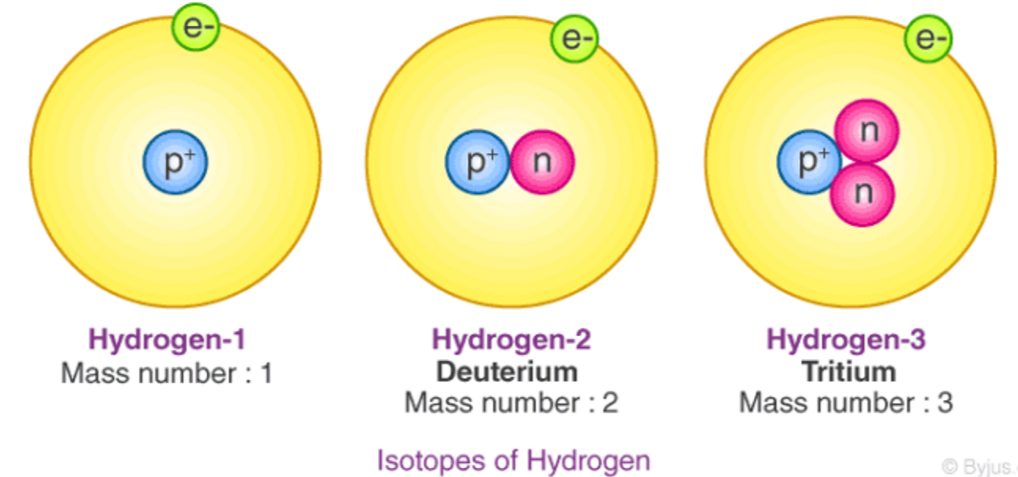
What are Isotopes?
A form of an element that has the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons
Stable Nuclei
Remain in the same form with the same number of protons and neutrons forever
Unstable Nuclei
Has too few or too many neutrons; The atom will exist for a while, but will eventually break up;
In relation to Mass
The atomic mass shown in the periodic table is the weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of the atom.
As the atomic mass of the elements increases, the ratio of neutrons to protons increases. Uranium has the largest naturally occurring nucleus, with 92 protons and over 140 neutrons.
What are Radioisotopes?
An unstable isotope that spontaneously changes its nuclear structure and releases energy in the form of radiation If an nucleus has more then 83 protons, no number of neutrons can hold it together forever