A measure of how fast a reaction is taking place The unit is
concentration is either appearing (positive rate) or dissapearing(negative rate)
Properties like mass, colour, volume, and pressure can be monitored to detect the amount (in mol) of reactant which disappears, or the amount of product that appears during a specific time interval.
Reaction Co-ordinate Diagram for the Formation of HBr
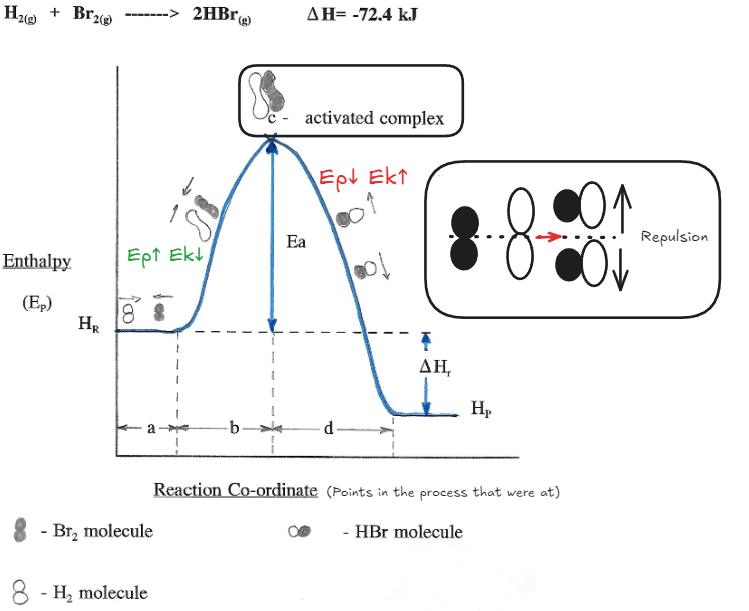
Activation Energy : the minimal starting energy (as changes to ) that the reactant molecules must have in order to undergo and effective collision and produce a reaction
Effective Collisions occur when the two colliding particles have enough and to overcome repulsive forces between positive nuclei and negative electron clouds.
- If the collision is effective, then old bonds break, and new bonds form
Section A
Both gases are in random motion and have a large quantity of kinetic energy Total potential energy stays the same because they are no where no each other
Section B
- Both molecules slow down when they approach each other because of the repulsive forces between molecules
- Kinetic is transformed in Potential
- Molecules stretch as the nonpolar covalent bonds within each molecule weaken
- This causes a large amount of energy to be absorbed
Section C
Activated Complex: a high energy, short lived intermediate configuration of reactant atoms.
- May decompose and form new lower energy stable products OR revert to the original reactant molecules
Section D
- H-Br molecules form, energy is released since bonds are forming.
- Potential drops and Kinetic increases
- Molecules speed up and move away from each other
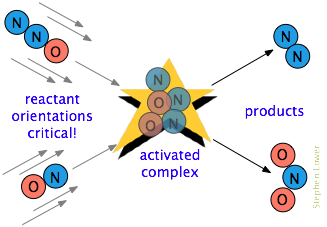
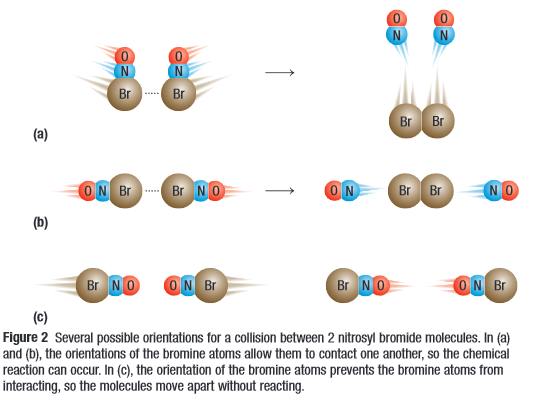
Collision Rate Theory
for a reaction to occur, two particles must collide. Reactants must also have enough kinetic energy and collide at a certain orientation.
Factors that affect the rate of reaction
The first 4 are for homogenous systems (reactants and products are present in the same phase)
Temperature
TLDR - Increasing the temperature of the reactants increases the rate of reaction
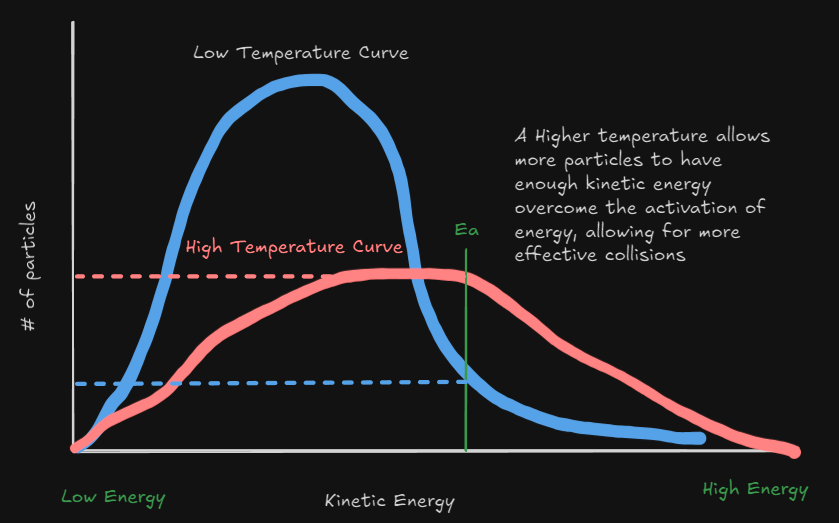 Increasing Temperature also increases the total number of collisions/second.
Increasing Temperature also increases the total number of collisions/second.
- The likelihood of effective collisions will also increase since more collisions will increase the number of geometrically effective collisions.
- Effects endothermic reactions more than exothermic
Nature of Reactants
TLDR - Increasing the complexity of reactants (more bonds) decreases the rate of reaction
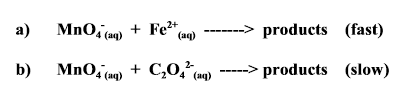
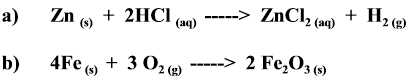
Energy is required to break the bonds between Carbon and Oxygen in Reaction b). So the formation of the products also takes longer.
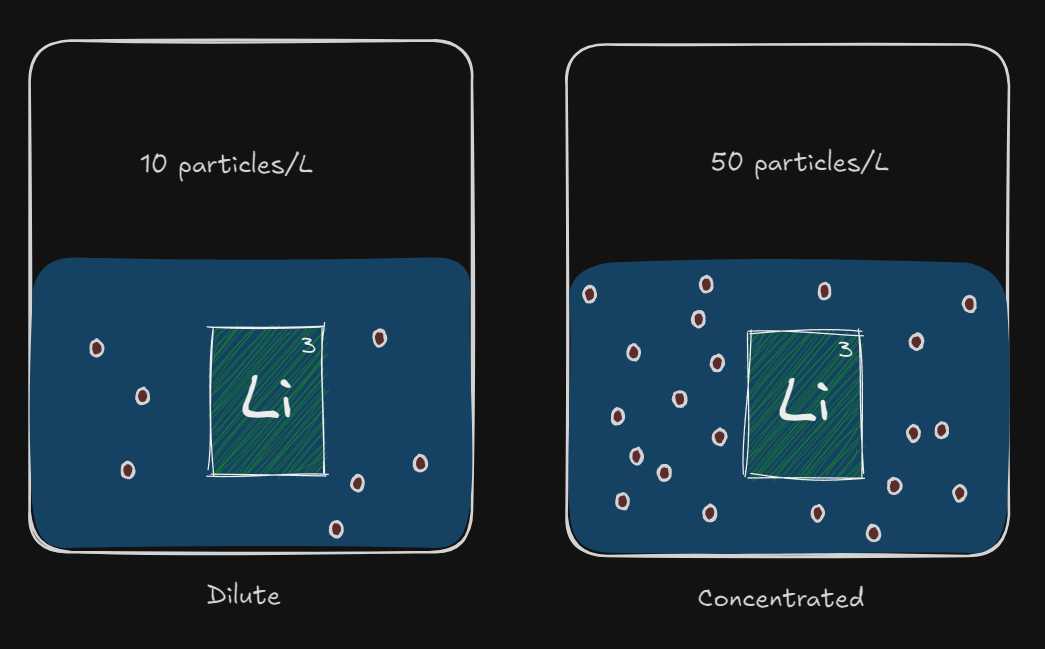
Concentration
TLDR - Increasing concentration of the reactants increases the rate of reaction
- This is because there are more particles present.
More particles = more collisions
more collisions = more effective collisions
more effective collisions = higher rate of reaction
Catalyst
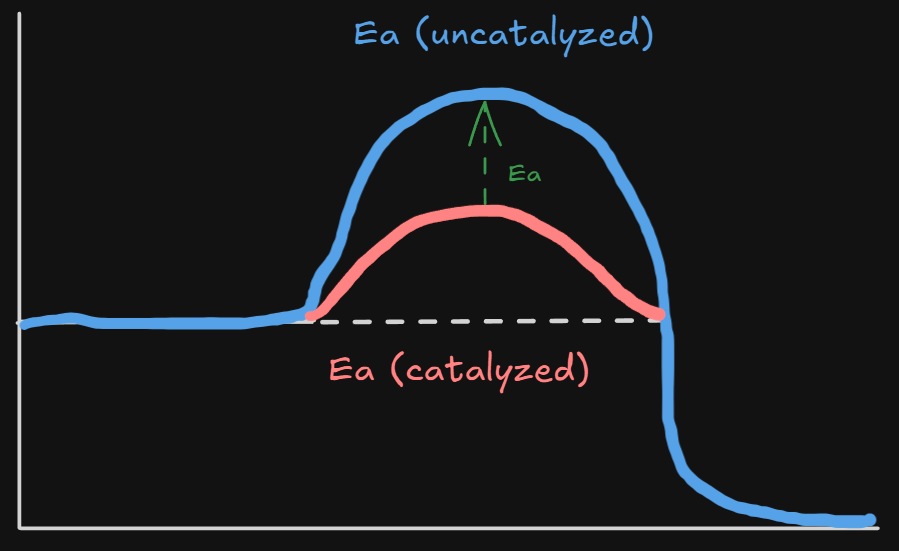
A chemical which speeds up a reaction by lowering the activation energy . It does not participate in the reaction. It acts as a surface for where the reaction can take place.
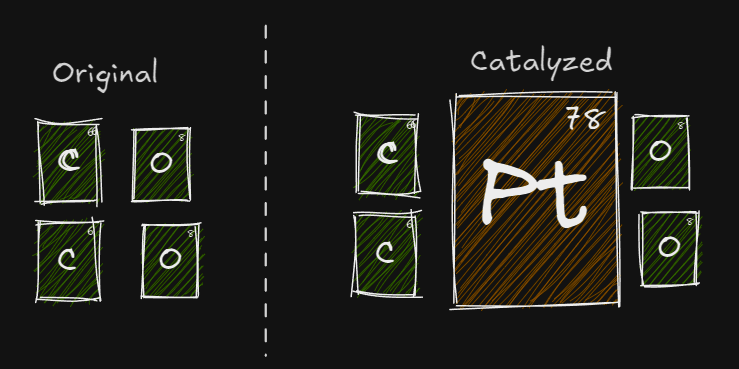
The catalyst is involved with the formation of a new activated complex which has a lower activation energy as compared to the original is the same since enthalpy is a state property independent from pathway
TLDR - Adding a catalyst increases the rate of reaction
Surface Area
TLDR - Increasing surface area of reactants increases the rate of reaction
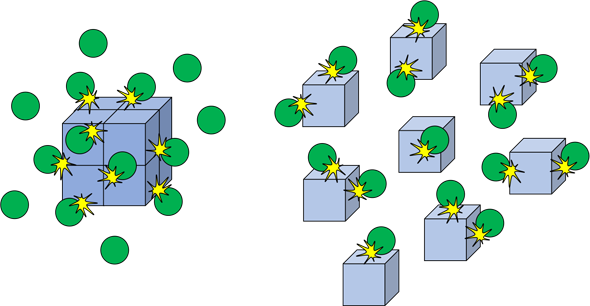
**A heterogenous system is one which involves reaction between reactants and products of 2 or more phases
In each case, the reaction will occur faster if the solid reactant is “ground up”
- This will add more reaction sites to the different types of particles, causing the number of reactions to increase