Also known as Thermal Energy. It is the sum of all Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy associated with particles of matter. We can never know the actual enthalpy of an element or compound, we can only calculate the difference between enthalpies.
NOTE
Potential energy is the energy stored within the particles and the bonds that hold them together. Kinetic energy is energy associated with the movement of particles
As Kinetic energy increases, Potential Energy decreases, vice versa
or heat is the amount of Thermal Energy transferred between substances during a physical, chemical or nuclear change.
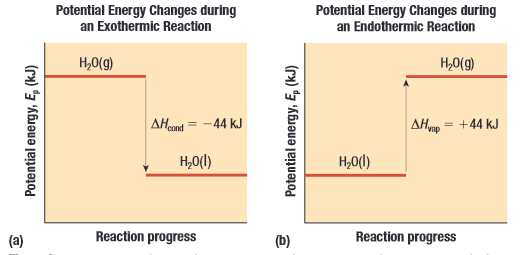
If then the reaction is endothermic, meaning it absorbs heat If then the reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat
NOTE
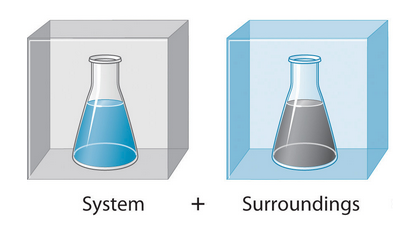
Enthalpy is only for a Chemical System, which is a group of reactants and products being studied. Surroundings may be in contact with the system but we’re not counting for it
Calorimetry
A process by which the energy changes of a system can be measured. Calorimeter: a device that can measure
is the Specific Heat Capacity of a substance
IMPORTANT
The energy absorbed by the water which is considered a surrounding, is equal to the Dont forget to reverse
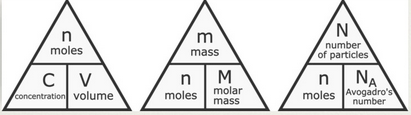
To find the energy released per mole of a reactant or product, find the mass ⇒ molar mass ⇒ moles of the compound, then do a mole-energy ratio.
A balloon of hydrogen gas will have molecules and it will have atoms
Important Formulas
Stoichiometry
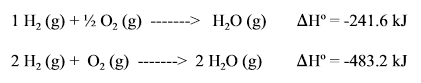 In this example, because there is twice as many reactants and products, will be 2x bigger.
In this example, because there is twice as many reactants and products, will be 2x bigger.
State Property
The enthalpy of matter depends on its state. Heat is a state property so it does not matter which path it takes to get from solid to gas for examples.
SATP
and
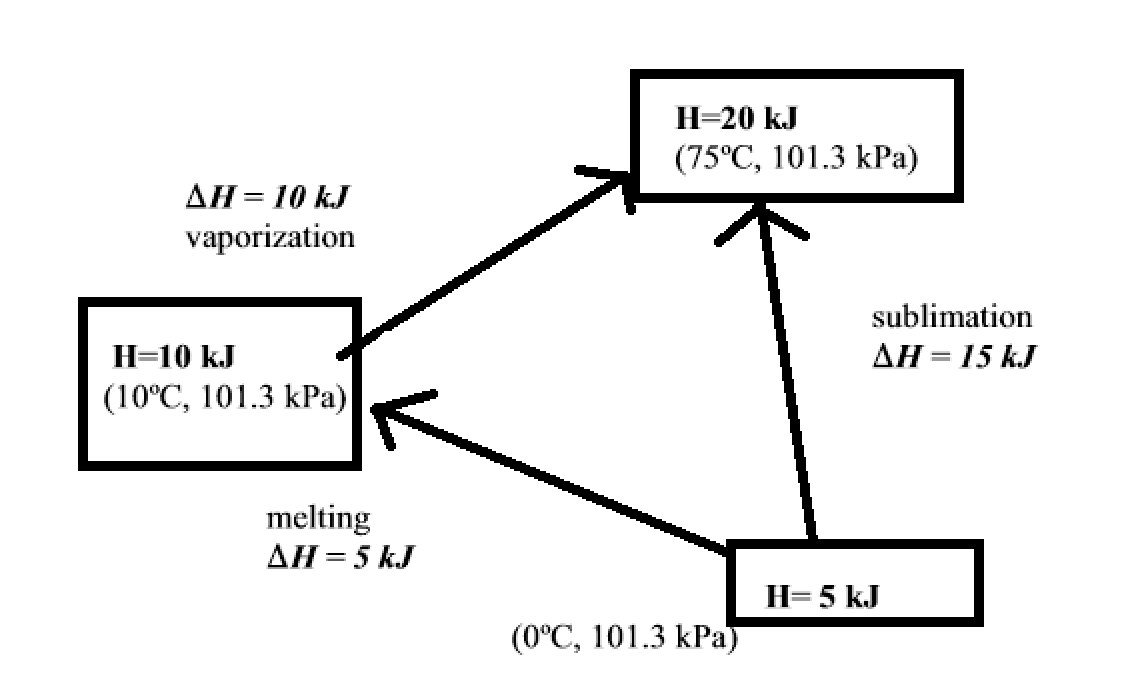
In this example, I could go from Solid to Liquid and then to gas. Or I could skip and go straight to Gas. It does not matter which path it I take.
assuming the amount of particles at each state stays the same.